常用布局
常用布局
# 添加布局
# 1. 利用XML文件设计
为了高效设计和开发,一般而言:
- XML文件中做界面设计
- Java代码做逻辑控制
# 2. 使用Java代码添加
为什么不用纯Java代码做布局呢?(可以做但一般不这么做)
因为代码不好控制布局样式,不能够灵活使用组件;完成简单的布局需要的不步骤相对较多,必须创建对象来进行设置,最终将此页面的布局对象传递给setContentView()方法

例如:创建布局,背景色为红色
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
// 1. 根布局为线性布局
LinearLayout linearLayout = new LinearLayout(this);
// 2. 设置宽高
linearLayout.setLayoutParams(new LinearLayout.LayoutParams(ViewGroup.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT,
ViewGroup.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT));
// 3. 背景为红色
linearLayout.setBackgroundColor(Color.RED);
// 4. 指定此Activity的内容视图为该线性布局
setContentView(linearLayout);
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
# 常用布局
- 线性布局
- 相对布局
- 帧布局
- 表格布局
- 网格布局
- 约束布局
# 线性布局-LinearLayout
重要属性:
- android:orientation(方向)
- android:layout weight(权重)

# 相对布局-RelativeLayout
相对某一位置作为参考,与视图的添加顺序无关
依靠参照物定位的布局,最灵活的布局。
重要属性:
<相对于父容器>
- android:layout_alignParentRight(相对父容器的位置)
- android:layout_centerHorizontal(是否水平居中)
<相对于其他控件>
- android:layout_toLeftof
- android:layout_alignRight

# 帧布局-FrameLayout
有层次的布局,控制多哥1控件的层次关系
重要属性:
- android:layout_gravity(控件重力)
- android:foreground(前景)
- android:foregroundGravity(前景重力)

# 表格布局-TableLayout
重要属性:
- android:stretchColumns(可伸展的列)
- android:shrinkColumns(可收缩的列)
- android:collapseColumns(可隐藏的列)

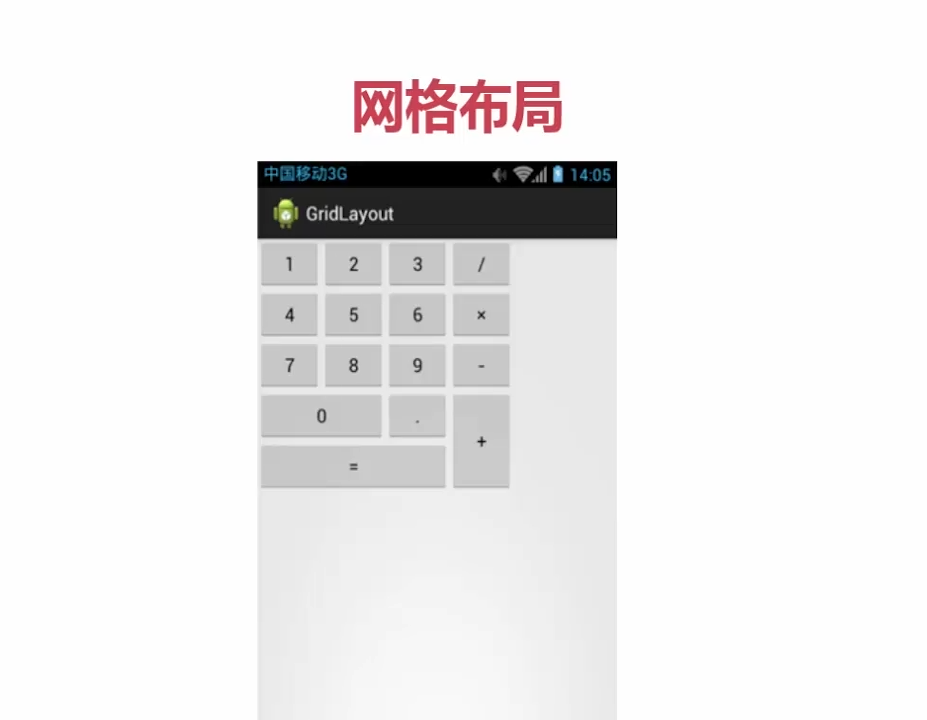
# 网格布局-GridLayout
重要属性:
- android:rowCount(行数量)
- android:columnCount(列数量)
- android:layout_row(位于第几行)
- android:layout_rowSpan(跨几行)
# *约束布局-ConstraintLatout

# 布局重要属性
- android:layout_width : 宽度
- android:layout_height : 高度
- android:layout_padding :内边距
- android:layout_margin : 外边距
【常量属性值】
match_parent: 父容器尺寸。当处于最外层没有其他元素时,此时为窗口的大小匹配wrap_content: 包裹内容。其大小会随着内容的增大而增大,最大不能超过屏幕尺寸
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_width="200dp" //直接给尺寸
android:layout_height="match_parent"
1
2
3
4
5
2
3
4
5
编辑 (opens new window)
上次更新: 2022/10/25, 23:13:03